What harm does cold weather have to the body? Experts warn that 5 parts may be affected
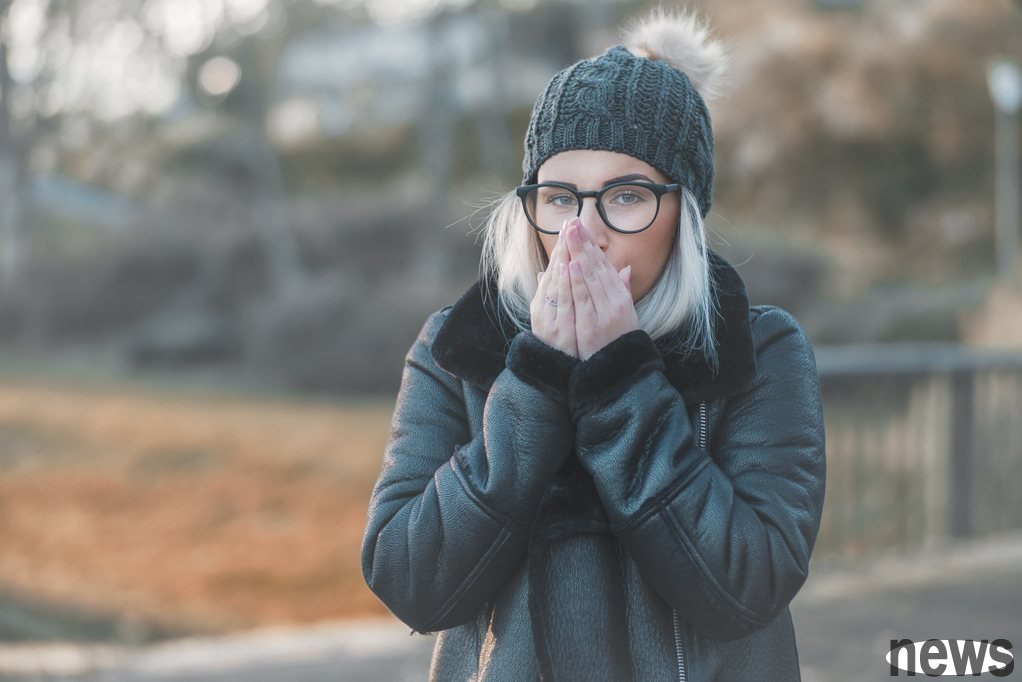

As the temperature drops in winter, cold weather is sometimes uncomfortable, but not only that, low temperatures can actually cause harm to physical health. Experts say that even if exposed to normal winter temperatures for a long time, it may affect the heart, brain and other important organs.
How can low temperature cause the body to lose heat?When the body is exposed to the cold, the heat loss rate may exceed the rate at which heat is generated. Over time, the body will consume as much energy as it has stored, causing the temperature to begin to drop. Exposed to the cold for a long time, especially when the core temperature of the body drops below 35 degrees Celsius, it may cause temperature loss, injury and other problems.
Cold weather affects all parts of the body, including:
1. Cardiology system experts point out that when the air temperature drops, blood vessels will shrink to prevent heat loss and maintain more blood around the body's core.When blood is moving from the outside to this area, this is why the fingers and toes become cold. But this increases blood pressure, and high blood pressure can cause heart disease to develop or moderate, especially those who are already facing higher cardiovascular risks. Extreme cold may also cause blood thickening and easier coagulation, which will also increase the risk of heart disease and medium wind.
2. Respiratory SystemExperts say that people with asthma, chronic lung disease or other respiratory diseases have higher risks when their temperature drops because cold and dry air can stimulate the respiratory tract, which can cause more inflammation and lead to muscle contraction around the respiratory tract, which may cause wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath or burning chest, especially when moving.
3. Immune systemGenerally speaking, cold weather makes people more likely to get sick.
Experts remind that when cold weather comes, people often gather indoors, and the more irritating environment makes bacteria easier to spread. More importantly, some viruses can survive better in the cold, and the human immune system may lose some of its effectiveness, such as dry and cold air that causes the mucosa covering the nose, mouth and throat to dry out, losing the ability to prevent bacteria.
4. Awareness functionVascular contraction caused by cold can affect the awareness function, especially when temperature failure occurs. When the core temperature drops below 35 degrees Celsius, there will be a loss of temperature. The lack of temperature may be caused by extreme cold, or in a less chilling temperature, if the body feels cold due to rain, sweat or entering cold water.
Symptoms of temperature loss include trembling, confusion, inequality, slow breathing, memory loss, lethargy, extreme fatigue, facial swelling or dysfunction, and skin whitening. Experts warn that temperature loss is a rush, and early warning signs like shaking should never be ignored.
5. Skin injuryExposure to the cold for a long time can also cause injury when the amount of blood flows to the limbs decreases. In addition, people with poor blood circulation are at higher risk. Signs of injury include numbness, skin whitening, red kidney or pain.
Once this happens, you should immediately leave the cold environment and enter a warmer place. Avoid friction and walking with damaged feet or toes, as this can cause more damage. On the contrary, the damaged area can be immersed in water that is not too hot.
How to keep warm?The first step to prevent the damage caused by cold is to wear clothes, especially when you go out for a long time, make sure that there is no skin exposed, such as wearing a scarf, hat and gloves, rather than just a coat.
Experts remind that even if going out in cold weather can help increase the temperature, avoid excessive physical activity because you will sweat and lose heat, which will get the opposite effect.
In addition, warm drinks may help people stay warm outside, but drinks should be avoided. Alcohol may make you feel warmer, but it can swell blood vessels and cause you to urinate more, resulting in irrigation. And alcohol interferes with thinking ability.
If trapped in a cold environment, experts suggest finding a place to protect the wind or stay alive to help keep warm.